Is CAR-T Therapy Covered by Insurance in the U.S.? (2026 Update)
Introduction
CAR‑T cell therapy (chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy) is one of the most advanced immunotherapy approaches in oncology: a patient’s T-cells are collected, genetically modified to target cancer cells, and then infused back to destroy malignant cells. With its promising outcomes especially for certain blood cancers, many patients ask: Is it covered by insurance in the U.S.? This article provides a 2026 update on insurance coverage, cost, reimbursement policy, and what patients should know.
What is CAR-T Therapy?
-
CAR-T therapy re-programs a patient’s own immune cells (T-cells) so they can recognize and kill cancer cells.
-
It has been approved for several hematologic malignancies (such as certain leukemias and lymphomas).
-
Because it is highly personalized, complex to manufacture, and often administered in an inpatient setting, it is very expensive. cellgs.com+2American Cancer Society+2
-
Because of its cost and complexity, reimbursement and access issues are important for patients and providers.
Does U.S. Insurance Cover CAR-T Therapy?
Medicare / Medicaid / Private Insurance
-
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has issued a National Coverage Determination (NCD) that requires Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) to cover FDA-approved CAR-T therapies when administered in accredited centers and according to the labeled indication. celltherapy360.com+1
-
For Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, coverage must be consistent with the NCD, but prior-authorization (PA) details may vary by plan. celltherapy360.com
-
For private commercial insurance plans: Many plans will cover CAR-T therapies, but coverage is variable depending on the plan, the patient’s condition, the therapy indication, network/center, prior authorization, and benefit design. BMT InfoNet+1
-
Medicaid coverage varies state by state: some states may cover CAR-T under their Medicaid programs; others may have more restrictive policies or require special approval. BMT InfoNet
2026 Updates / Reimbursement Policy Changes
-
For FY 2026, CMS finalized policies affecting CAR-T (and other cell/gene therapies). In the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS) rule, CMS increased the MS-DRG (Diagnosis-Related Group) base payment for CAR-T stays by about 16.8% (or approximately 17%). Avalere Health Advisory+1
-
Medicare will continue to use the current MS-DRG grouping for CAR-T cases and manufacturing costs are bundled rather than separately reimbursed for individual steps. Holland & Knight+1
-
Some legislative activity: for example, a bill (FL H0725) indicates changes for insurance policies issued on or after Jan 1, 2026 regarding CAR-T therapies in Florida. BillTrack50
What This Means for Patients
-
If you are eligible (i.e., your cancer type and line of therapy match the FDA indication), and you’re treated at an accredited center, the major payers should cover the infusion of CAR-T therapy.
-
However: You must still check benefits, prior authorization, network provider, center accreditation, and understand your out-of-pocket costs (deductible, copay, coinsurance).
-
Non-drug costs (hospital stay, ICU, supportive care, travel/lodging) may still impose financial burden. BMT InfoNet
-
Even when coverage is approved, the center’s financial team should verify and assist with payer approval and coordinate with the therapy manufacturer’s patient assistance or support programs.
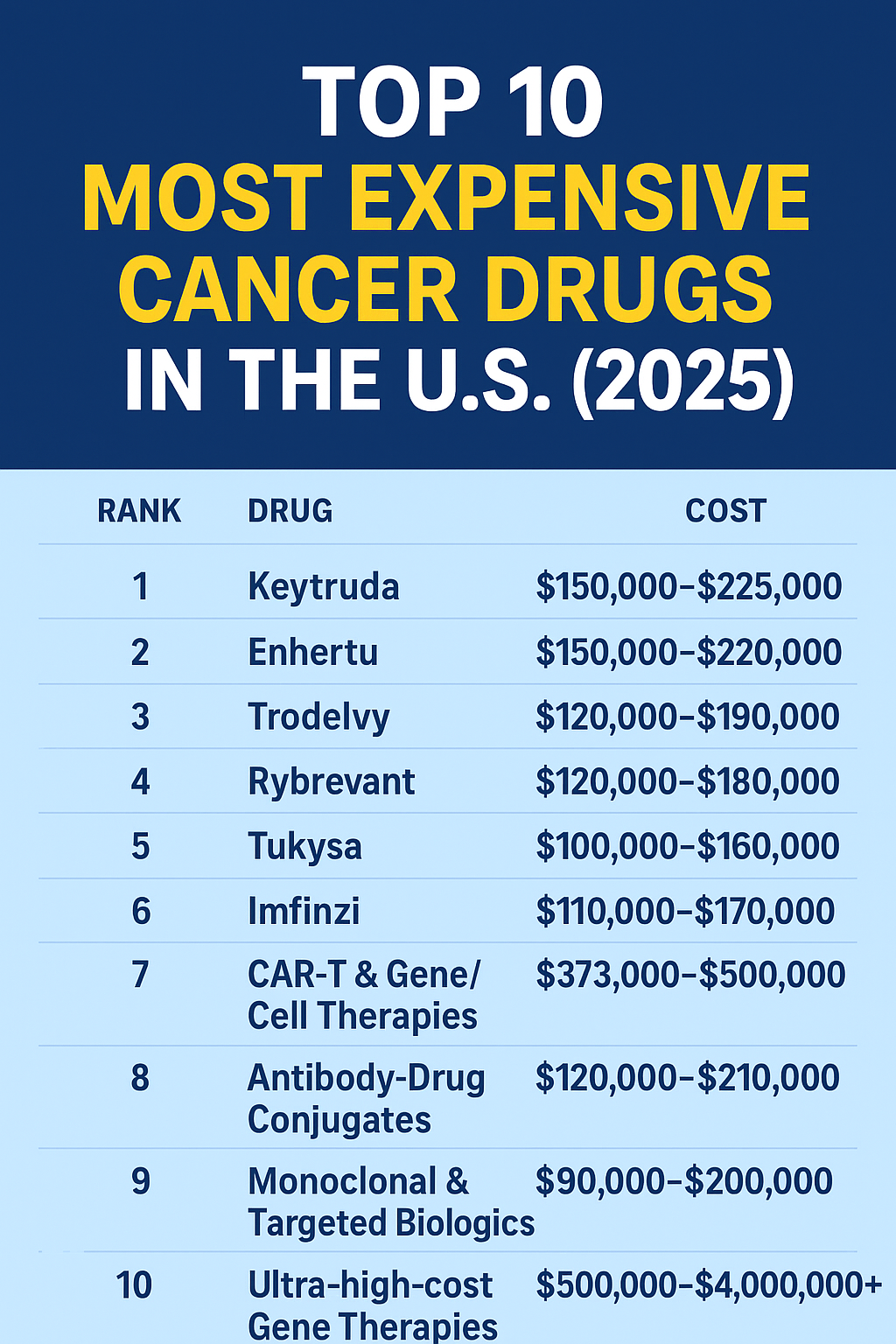
Cost of CAR-T Therapy in the U.S. (2026 Update)
Here is a table summarizing typical costs of CAR-T therapy in the U.S.:
| Item | Approximate U.S. Cost* | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| List price of CAR-T product alone | $373,000 – $475,000 for many treatments. untravel.info+3car-t-access.org+3Israeli Hospitals+3 | Does not include hospital stay, ICU, complications. |
| Real-world median cost (commercial insurance) | ~$402,500 for the CAR-T product; median total cost ~$608,100 for peri-therapy period (≈ 41 days before to 154 days after). OUP Academic | “Peri-CAR-T” includes hospital stay, apheresis, ICU, readmissions. |
| Total cost including hospitalization & complications | For some patients > $1 million. OUP Academic+1 | High variation depending on complications, ICU stay, outpatient vs inpatient. |
| Average cost range when including other associated costs | ~$300,000 to $600,000 or more in many U.S. references. BioInformant+1 | Indicates scope of variation. |
*Costs reflect U.S. figures as of 2024-2026; actual cost may vary by center, state, insurer, and complications.
Why So High?
-
Manufacturing process is complex: individual T-cell collection, engineering, expansion, quality testing, shipping. cellgs.com+1
-
The therapy is often delivered in hospital/inpatient setting, with ICU stays for complications (cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity). OUP Academic
-
Because the eligible patient pool is relatively small (relapsed/refractory cases), cost per patient is high. car-t-access.org+1
-
Hospital resource use, follow-up care, supportive therapies add to total cost.
Popular Similar Websites & Resources
Below is a table of several websites that address insurance coverage, cost, and access of CAR-T therapy. These can serve as further reading and references.
| Website | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| BMT Infonet – Insurance & Financial Planning for CAR-T | Patient-oriented site with information on coverage, out-of-pocket costs, assistance programs. BMT InfoNet | BMT Infonet – Financial Considerations: CAR-T Cell Therapy |
| Cell Therapy 360 – Patient Access & Insurance Coverage | Coverage outline for CAR-T products (manufacturer site) including benefit verification tools. celltherapy360.com | Cell Therapy 360 – Insurance Coverage |
| American Cancer Society – CAR-T Cell Therapy | Overview of CAR-T, costs, how it is paid for, what to ask. American Cancer Society | American Cancer Society – CAR-T Cell Therapy |
| Advisory (Avalere Health) – New CAR-T Policies Affect Access & Reimbursement | Professional/industry article about payer policy changes for FY 2026. Avalere Health Advisory+1 | Avalere Health – New CAR-T Policies |
Key Considerations / What Patients Should Ask
-
Does my insurance plan cover the specific CAR-T therapy I need (for my disease type and line of therapy)?
-
Does the treatment center have accreditation and is the therapy approved by the manufacturer under required programs (e.g., REMS, certification)?
-
What is the prior-authorization process, and what documentation is required from my oncologist/center?
-
What portion of costs will my plan pay, and what will my out-of-pocket (deductible, copay, coinsurance) cost be?
-
Are there additional costs (hospital stay, ICU, travel, lodging, caregiver) not fully covered by insurance?
-
Is there a patient assistance program through the therapy manufacturer that can help with costs, lodging, travel?
-
If I live in another state than the treatment center, how will that affect my coverage, travel, lodging, etc?
-
If complications occur (e.g., ICU, readmissions), how is coverage handled for those?
-
If I’m on Medicaid, what are the state-specific requirements and coverage limitations?
-
What is the expected timeline: from apheresis to infusion, how long hospital stay, what follow-up care is required?
20 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) and Answers
-
Q: What cancers are approved for CAR-T therapy in the U.S.?
A: CAR-T therapies in the U.S. are approved for certain relapsed or refractory hematologic malignancies (for example, large B-cell lymphoma, some leukemias, mantle cell lymphoma, multiple myeloma in certain cases). Approval specifics depend on the product label and the regulatory status. -
Q: Will Medicare cover CAR-T therapy?
A: Yes — Medicare Fee-for-Service covers FDA-approved CAR-T therapies under the CMS NCD if administered in an accredited center and per label. But you must confirm eligibility and the specific product. celltherapy360.com+1 -
Q: Does private insurance typically cover CAR-T therapy?
A: Many private plans do cover CAR-T, but it depends on the plan, disease indication, treatment center, and prior-authorization. You must check your benefit plan. BMT InfoNet+1 -
Q: What if my insurance denies coverage?
A: You or your provider can appeal. Also check for manufacturer assistance programs, patient advocacy groups, and explore clinical trial options. -
Q: What are my out-of-pocket costs likely to be?
A: While the product cost is hundreds of thousands of dollars, many patients’ out-of-pocket amounts (deductible/coinsurance) may be more modest (e.g., median ~$510 in one study) but there can be substantial non-drug costs (hospital stay, lodging, travel). OUP Academic -
Q: Does Medicaid cover CAR-T therapy?
A: Sometimes — coverage depends on your state Medicaid program. Some states may require additional approvals or have restrictions. -
Q: Are there any geographic restrictions on where I can get CAR-T therapy?
A: Yes. The center must be accredited for CAR-T administration, and your insurance may require treatment to be at an “in-network” center. Travel and lodging may be additional costs. -
Q: How long does the hospital stay for CAR-T therapy typically last?
A: In one study, median length of stay was ~15 days for inpatient delivery. OUP Academic ICU stay for some patients is common due to potential toxicities. -
Q: Are there risks or side-effects with CAR-T therapy?
A: Yes. Some of the key risks include cytokine release syndrome (CRS), neurological toxicities, infections, prolonged immunosuppression. These side‐effects affect cost, hospitalization length, and follow-up care. -
Q: If the therapy fails or I relapse, will insurance still cover further lines of treatment?
A: That depends on your insurance plan, but many plans cover additional lines of therapy. However, coverage for additional CAR-T therapy or retreatment may be more uncertain — you should check policy details. -
Q: Is CAR-T therapy always a one-time treatment?
A: For many approved indications it is given as a one-time infusion (plus follow-up). However, new studies, retreatments, or combinations may change this. -
Q: Will the high cost mean I personally will pay hundreds of thousands?
A: Unlikely for most insured patients — while the list price is extremely high, insurance (public or private) covers most of the cost. Your personal payment would typically be your share (deductible, coinsurance) plus non-covered expenses. -
Q: Can uninsured or under-insured patients access CAR-T therapy?
A: It is significantly more challenging. Some centers may require financial clearance; manufacturer patient assistance programs may help; clinical trials might offer access; philanthropic/charity support may be available. -
Q: Are there payment or reimbursement models based on outcomes for CAR-T therapy?
A: Yes, value-based reimbursement models are a topic of discussion (e.g., payment tied to patient outcomes) given the high cost and significant efficacy variation. Drug Discovery Trends+1 -
Q: Will out-of-pocket travel and lodging costs be covered?
A: Often these are not fully covered by insurance. Patients should ask the treatment center about lodging programs, patient advocacy funds, or ask if the manufacturer has support programs for lodging/travel. BMT InfoNet -
Q: Does coverage differ if therapy is delivered outpatient versus inpatient?
A: Yes, delivery setting can affect cost, reimbursement, and resource use. Inpatient stays generally cost more. Coverage policies may differ depending on whether the center treats outpatient/inpatient. OUP Academic+1 -
Q: Is experimental or off-label CAR-T therapy covered by insurance?
A: Usually not covered if it is non-FDA approved or off-label; such treatments may be available in clinical trials (which can reduce patient cost). -
Q: How can I find if my insurance plan will cover a specific CAR-T therapy?
A: Contact your insurance provider and ask for prior-authorization requirements; ask your treatment center’s financial navigator or case manager to run a benefits verification; also ask the manufacturer for assistance tools. celltherapy360.com -
Q: Has the reimbursement policy for CAR-T therapy changed recently?
A: Yes. For example, for FY 2026 CMS increased base payment rates (~17 %) for CAR-T cases. Also manufacturing cost and reimbursement policy changes have been implemented. Avalere Health Advisory+1 -
Q: Should I delay therapy until my insurance approves or changes policies?
A: If you have a CAR-T eligible disease and your oncologist recommends it, delaying may not be advisable. However, ensure benefit approval and financial clearance by the center to avoid unexpected costs. Always discuss timing with your clinical and financial team.
Summary & Take-Home Points
-
CAR-T therapy is generally covered by major payers (Medicare, many private insurers) in the U.S., provided FDA-approved indication, accredited center, and prior authorization.
-
Coverage is not automatic — verifying benefits, prior authorization, and understanding out-of-pocket costs is essential.
-
The list price and real-world cost of CAR-T therapy are extremely high (often hundreds of thousands of dollars, in many cases over $500 K to $1 M), but insurance shields many patients from bearing the full cost.
-
Policy changes for 2026 (e.g., CMS reimbursement increases) suggest a shifting reimbursement landscape, possibly improving provider access and coverage.
-
Patients must also consider non-therapy costs (hospital stay, travel/lodging, caregiver support) and work closely with treatment center financial navigators and manufacturers’ assistance programs.
-
It remains critical to act early: if you’re being evaluated for CAR-T therapy, engage your insurance, your treatment center’s billing/financial team, and your care team to ensure the coverage path is clear.
1. Coding & Billing Updates
-
The American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) publishes a “CAR-T Coding and Billing Guide” (latest update April 2025) that includes detailed HCPCS/CPT/ICD-10 codes, inpatient vs outpatient billing rules, and payer-specific nuances. astct.org+1
-
For example: For DOS (date of service) on or after July 1 2025 a new HCPCS code Q2058 is effective for the product Obecabtagene autoleucel (“obe-cel”). CMS
-
Medicare’s “Billing Instructions” for CAR-T detail outpatient (Part B) vs inpatient (Part A) payment rules and product-specific Q-codes. FCSO Medicare+1
2. Coverage Requirements: National Coverage Determination (NCD)
-
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) maintains NCD 110.24 which specifies that autologous CAR-T therapy is covered when administered at FDA-approved indication, in a facility meeting REMS/REMP requirements, etc. CMS+1
-
Note: If any requirement is not met (e.g., off-label use, non-accredited facility) then non-coverage applies. CMS
3. Reimbursement & Payment Policy Trends
-
In the FY 2026 inpatient prospective payment rule, CMS proposed a ~17 % increase in the base payment for CAR-T inpatient stays (via MS-DRG specific for CAR-T) to better align reimbursement to high cost care. Avalere Health Advisory+1
-
The “New Technology Add-on Payment” (NTAP) pathway remains relevant for cell & gene therapies: CAR-T products may qualify if they meet “newness”, cost criteria, and substantial clinical improvement requirements. CMS+1
4. Innovative Payment / Value-Based Models
-
Because of the high upfront cost and uncertain long-term outcomes, many payers/manufacturers are exploring outcomes-based reimbursement (OBR) or risk-sharing models where payment depends on patient results. ipghealth.com+1
-
For example: In European markets (and increasingly in U.S discussions) CAR-T deals include rebates or installments tied to remission or durability of response. BioInsights Publishing+1
-
The CMS “Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) Access Model” (Request for Applications March 2024) signals future U.S. pilot programs linking payment for CGTs to outcomes or performance metrics. CMS+1
5. Cost Variation & Real-World Data
-
A study of Medicare claims found that for inpatient CAR-T therapy the average cost was ~$498,723 (range ~$276K-$1,066K) and for outpatient setting ~$414,393 (range ~$276K-$849K). PMC
-
The total cost including pre- and post-therapy period can vary widely, underscoring the importance of verifying total care costs beyond just the product.
6. Provider & Hospital Considerations
-
Many hospitals report that even with current reimbursement, CAR-T‐related costs can exceed what payers reimburse, leading to financial risk for providers and potential access barriers. /+1
-
The American Association of Blood Banks (AABB) in 2024 urged CMS to adopt payment policies that better reflect the multidimensional resource use of CAR-T (e.g., cell collection, manufacturing, ICU stays). AABB
7. Access & Market Trends
-
The overall “Cell & Gene Therapy Patient Access and Reimbursement Market” indicates that CAR-T therapies captured about 60 % of the CGT segment in 2024 in North America and growth is expected. Precedence Research
-
Trends show payers increasingly willing to engage in value-based / alternative payment models to handle the high cost of one-time curative therapies. Brookings
Suggested Additions to Article
When you update your article, you may wish to include:
-
A small section titled “Coding & Billing Updates (2025-2026)” referencing the ASTCT guide and new HCPCS codes (e.g., Q2058).
-
A section titled “Innovative Reimbursement Models for CAR-T” explaining outcomes-based reimbursement, value-based contracting, and how that might affect access/coverage in the U.S.
-
Some commentary on provider/hospital burden and how reimbursement insufficiencies may affect access.
-
A note on Medicare vs Commercial vs Medicaid payer differences in access, coding, and reimbursement.
-
Real-world cost figures beyond list price, e.g., the Medicare claim averages.







Add a Comment